Software name : Avidemux
Software version : 2.4
- Extract Subtitles From Iso
- Extract Subtitles From Dvd Ubuntu Usb
- Extract Subtitles To Srt
- Extract Subtitles From Dvd Ubuntu Media Player
- Get Subtitles From Dvd
So far the process has been to use one of a number of methods to make a direct copy of the DVD to an ISO, then use VobCopy to extract a single VOB, containing the main content, to a file. To make the ISO, I’ve tried DD (doesn’t work reliably) and the optical device equivalent (forget its name but it works). I want to use the command line to extract subtitles from video files. I want to extract subtitles from a lot of files. That is why I want a CLI tool. Ideally it should work with any video format that supports embedded subtitles. For example: subextract -f RevolutionOS.mp4 Extracting English.srt Extracting French.srt Extracting Russina.srt All. That is, getting the image subtitles from a DVD into a SRT text file. You can rip the DVD with any DVD ripping tool, creating a /vob directory on your hard drive. Then install the transcodepackage and run tccat -i /home/user/rip/vob tcextract -x ps1 -t vob -a 0x22 subs-en. In this particular case, the 0x22stands for English. Farhad Mohammadi Majd (2018-03-08): $ ffmpeg -i VTS011.VOB Do not do that. Never access the VOB files in a DVD-video structure directly, they do not contain only the title video data but also menus and garbage. You can use tools/dvd2concat to extract only the parts of the VOB file that matters. Or MPlayer to dump them into a file.
Extraxt subtitles from.mp4 To extract subtitles from.mp4 files that have subtitles embeded you can use the command line tool ffmpeg to install it use: sudo apt install ffmpeg (on older ubuntu use.

If you want to extract subtitle files from a DVD you should understand a little how they work. Subtitles in DVDs are contained in VOBfiles along with the main video and audio streams. We can call them all streams here to account for the difference between a self contained file and a stream. Several streams can be included in a file.
The subtitles you see on a DVD are streams of images files which appear one after the other. Each stream displays a different language. When we extract these streams of subtitles the most handy format we can save them as is actually a text file which has the timecode of when the text appears. If the subtitle file you have is in text rather than image format it makes it easier to edit it and translate it. You can easily send that file via the internet or put it on a website for others to download.
In order to create a text-basedsubtitlefile we first need to extract the images files from the DVD to two files:
- an *.idx file which has the time code of the image subtitles (this is called a VobSub file)
- and a *.sub file and contains the image information.
We can then convert those files into a single text based subtitle file. There are many different formats but Avidemux uses a very compatible one with the '.srt' extention.
note : Screenshots in the following explanation are a combination of Ubuntu (Linux) and Windows operating systems. Avidemux works well in both and the interface looks the same except for a few color differences.
Extracting to an idx / VobSub file
From the Tools menu select 'VOB' and then 'VobSub'
Then you should see the following screen asking you to Browse for three things.
- VOB file(s)
- IFO file
- VobSub file
Finding the VOB Files
When you click on the first Browse button in the above image we are asked to browse for the VOB files :
However sometimes it's not that clear where they are. The files we want are in a folder on the DVD (if you are doing this for files on a DVD) called VIDEO_TS folder.
Normally for a short film there is only one VOB file with video data in it. For longer films there is normally more than one, because there is a maximum file size for the VOB files.
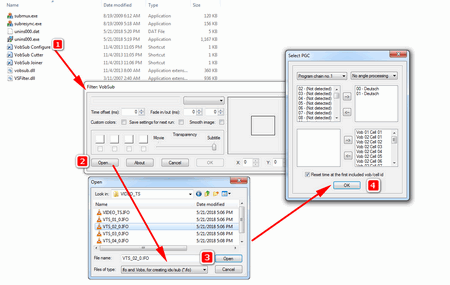
Let's have a look at a complicated DVD structure. There are some small entries in the structure which are system files and files for the menu - we should ignore these. The files with the video, audio and subtitle files we need are the big ones. They start with names like VTS_02_1.VOB,VTS_02_2.VOB, VTS_02_3.VOB, VTS_02_4.VOB. If you click 'Browse' next to 'VOB Files' then you should browse to the appropriate directory ('VIDEO_TS') and you should see something like this :
For this task we need to select the first big VOB which in this case is VTS_02_1.VOB. The ones following it will be selected automatically. When you have selected the right one click on 'open' :
Locating the IFO file
If you click on the second button :
you will be asked to look for the IFO file. The IFO file has information on what language the different subtitle streams are, so we need to browse to find this file. If there is more that one IFO file in the DVD we need find the one that has the same beginning as the large VOB files. In this case it is VTS_02_0.IFO
When you have found it click on 'open' :
Select where to save the VobSub files
The third button :
will ask you to browse for a place to save the VobSub file. When you have found the right directory write the name of it in the box next to 'Name:' and make sure it ends with '.idx'. The below is an example (you can use any name, 'subs' is just my example) :
When you have done this, and if the other three boxes are complete, then press 'Save' :
Saving your files
When you have found or selected all the files. Then click 'OK' to shut the small window with the small buttons :
and you'll get a window telling you how long the process will take.
When this process is complete you will have created a new .idx file and and new .sub file. These will be saved in the directory you choose for saving the .idx file. In my case I saved them to the desktop :
Making the '.srt' File
Now we want to merge the idx file and the .sub file into a '.srt' file. Click on the top menu 'Tools' and then 'OCR (VobSub -> Srt)':
You should see a window titled 'MiniOCR'.
Click on the 'Open' button under 'VobSub'. You will then see a window called 'VobSub Settings'.
Click on 'Select .idx' and browse for and select the idx file you created in the 'Extracting to an idx / VobSub file' section.
Click on 'Open' when you have selected the idx file. You should return to the 'VobSub Settings' window :

Extract Subtitles From Iso
If the DVD you are using has more than one language it should be displayed in the 'Select Language' drop down box. Select the language you want to create a subtitle file for.
When you have the right language selected click 'OK', and you should return to the 'MiniOCR' window. Now you need to select a place on your computer to save the target *.srt file to. Click on the 'Save' button in the 'Output srt' section :
You will see a window asking you to choose a folder to save the srt file in.
'
Browse until you find the right place. When you have, give the file a name by typing in a name in the box at the top
make sure the name ends in '.srt' and then click 'Save'
Now you have set your input and output files you can start the process of converting the images file in to a text file. This process is called OCR. Click 'Start OCR'.
You should see a window like this:
The OCR (Optical Character Recognition) process needs you to tell it what the characters (letters and numbers + symbols) in the subtitles are. It will display a character from the image subtitle and you have to then tell the application what the corresponding text character is. Avidemux will show you a phrase and one character for that phrase like this:
Now you must type the right character in the empty text field.
You do this because it is more accurate for you to specific exactly what the characters are than for the application to guess.
Where it says 'Current Glyph Text:' and shows an image of a character you need to enter that character using the keyboard in the box below and then click 'OK'. It does make a difference if it is a capital letter or a lower case letter. Also this process is very unforgiving at the moment. There is no undo option, so don't get it wrong!
Sometimes 2 characters well be selected. You should enter those two characters and click enter. This may seem to be taking a long time but when you have entered all the characters and numbers the program should fly through the subtitles. You should be able to process a 90 minute film in 5 -10 minutes.
When you are finished the '.srt' file you saved will have the right timecode and subtitle information in it. You can open it with a text editor and it should look something like this:
Updated 25/06/2014Home » Guides » Ripping subtitles from hardsubbed video with SubRip
How to extract subtitles from a hard-subbed video into SRT format using SubRip.
Some video files have subtitles 'burned into them'. SubRip can be used to extract the subtitles as text, as well as save them as bitmaps for later removal. This guide shows you how to extract the subtitles.
Open the video file by clicking on the button encircled in red below, or selecting Open Hard Subbed Video files fromthe File menu:
SubRip will try to open any file that AviSynth supports, but it can only detect the frame rate of .avi files. If you open another kind of file, SubRip will ask you to input the frame rate:
Please note that, in addition to AviSynth, you also need to have the appropriate codecs and filters installed. For example, to open DVDs, you need DGMPGDec. SubRip creates a file named 'temp.avs' in its directory. The rule of thumb is: if you cannot play that file in your favorite media player, then neither will SubRip be able to open it. Also, some codecs and filters do not provide the ability to seek to an arbitrary frame. Normally, SubRip only moves forward, but it occasionally needs to seek to the first frame of a subtitle after changing the detection settings. AviSynth seems to have its own buffering, but only between the previous and next keyframes. If you notice that seeking is inaccurate in some particular video file, the best approach is to convert it to an .avi file.
The Video file viewer window opens. Use the track bar or the edit box encircled in red below to move to a frame where you can see subtitles. Alternatively, press the Play button and let the video play, then Press the Pause button to stop the video when yousee a subtitle, preferably with two or more lines.
Right-click and drag to define a rectangle around the region where the subtitles appear. Make it large enough so that it encloses the subtitles and has enough room on either side for cases when the subtitles occupy a larger area. You can then resize the window to take less space and show only the subtitle region as in the image below. Be careful for cases when there are more lines in the subtitle. You can always stop processing and redefine the region byright-clicking and dragging.
The area encircled in red above shows the Text and Outline Colors. The three colored rectangles in each group show the darkest, detected, and lightest color respectively. Move the coursor inside the rectangle defined earlier (the cursor cnanges into a cross). Left-click INSIDE a character (its white area) so that SubRip can detect the Subtitle Color and Width. Look at the area circled in red above to confirm: the detected colors should match what you see in the video window. If not, click again inside another character. Try one that has a vertical line, like 'L', 'l', 'd', 'h', etc., and click inside the vertical line. The Width boxes should typically show values between 1 and 5 pixels. Anything larger would probably mean that detection was unsuccessful. These values are used for validation, and limit how far around a pixel SubRip searches for neighbors of a similar color. You can also set or change the colors manually by clicking inside the middle (larger) rectangles in the area encircled in red above.
If after several tries the detection still does not seem to work, press the button encircled in red below to show the Advanced Color Options panel. Then, try lowering the Text Color Tolerance values (the color of the outline may be too similar to the color of the text). You can change the Tolerances for all color channels simultaneously (if the checkboxes in the rightmost column are checked) or for each color channel individually. For example, if the subtitles are white and the outlines are blue, you may want the color tolerance in the blue channel to be larger, to compensate for the blurring caused by compression. The Outline Color can be used to restrict false guesses: only pixels of the Text Color that are close enough to pixels of the Outline Color are marked as text. The size of the exploration window is the Outline Width value. If the subtitles do not have an outline, simply uncheck the Use outline color checkbox and adjust the Text Width value manually, after verifying that the text color in the colored rectangle looks correct.
In the main window, a rectangle the size of the selected region will appear, with the subtitles in white and the outlines in red, as shown below. If the subtitles do not have outlines, fake red outlines are added based on proximity to white areas. If the subtitles do not show up properly (the lines are too thin, or irregular), try playing with the Text and Outline Widths or increasing the Text Color Tolerance value. Ideally, even on a bright background, you should only see the text in white in the main window. If large bright areas also show up as white, try checking the fill open and large areas checkboxes. Open areas include areas that touch the border of the rectangle, shown below in green. Large areas are areas that are taller or wider than a character (10 times the value in the Text Width field), shown below in gray. Note that the large areas on the left are still white, because they are not large enough. You can try lowering the Text Width value to compensate.
Extract Subtitles From Dvd Ubuntu Usb
If the subtitles always appear at the same position during the video, press the button encircled in red below to show the Inter-line Options panel. Check the Draw lines on top checkbox. Leave the Fill sides checkbox unchecked for now.
Set the Line Count to how many lines of text there are in the subtitle. Next, adjust the Top line offset so that the top blue line just about touches the top of the highest character on the top line. If the Fill open areas checkbox is checked, areas that touch the blue lines are also considered open, and will be filled with green, so you need to set the Top line offset value so that all characters are still white. This helps eliminate false guesses when the background behind the subtitles is white. Next, set the line Height so that the second blue line just about touches the bottom of the lowest character on the first line. Finally, set the Space value so that the bottom of the second blue line just about touches the highest character of the second text line. The final result should look like the image below. Note that the large areas on the left are now green, because they are considered open areas, since they touch the blue line between the subtitles. Also, the Line Height value set here will be used in the routine that fills large areas.
Finally, you may try checking the Fill sides checkbox in the Inter-line options panel. Select the Text Alignment. This option tells SubRip to start from the left, middle, or right, and fill the areas where it can't find white pixels close enough to other white text areas with fuchsia. The final result should look like the following image:
This particular frame is a very bad case, because of the white objects behind the text. The previous image was obtained without using the Outline Color as a guide (the Use outline color checkbox was not checked). The next image shows what happens in this frame when the Use outline color checkbox is checked. Notice that there are white areas that are not text.
This problem can sometimes be solved by lowering the Text Color Tolerance values, but that may lead to very thin or irregular characters, as shown below. This is a problem because thin characters may become disjoint or may be skipped altogether if the values in Options -> Advanced OCR Setup -> Character Setup are small. Also, irregular ('eaten by ants') characters will require you to type in the correct text a lot more frequently.
Extract Subtitles To Srt
Instead, by leaving the Text Color Tolerance values high (>50), and setting the Text Width high also (>5), the entire background area is interpreted as text, but becomes large and is filled with gray, as in shown the next image. The color does not 'bleed' into the letters because of the outline, but that is not always the case. Also, increasing the Text Width value signifficantly slows down processing, because the exploration window is larger, so only use this combination of settings when everything else fails.
Another way to deal with thin and irregular characters is to use the Fatten text feature. The image below shows the result. Notice that the characters are thicker. This also helps reduce the number of times you need to type a character in the New character(s) window. The process is controlled by the Fatten Color Tolerance values in the Advanced Color Options panel. The values for each color channel are relative to the darkest and lightest Text Colors. They control how different a pixel's color can be from the Text Color in that channel in order to still be considered for fattening. The darkest and lightest Fatten Colors can be seen as colored rectangles right below the darkest and lightest Text Colors. If the subtitles have outlines, these tolerances should be larger in the color channels that have larger differences between the Text Color and the Outline Color.
The purpose of this entire process is to make only the text show up as white in the image. Several frames are then accumulated into a black and white image, and the other colors are ignored. The Same sub tolerance value tells SubRip by how much the number of detected white pixels should vary from frame to frame in order to conclude that the subtitle has changed. The Min. pixels value tells SubRip what is the minimum number of white pixels that need to be detected to trigger processing. The image that the OCR process is run on looks like the one shown below:
When you are satisfied with the detection parameters, press the Rew. button to go to the start of the video, then the Run button to start the OCR process. The OCRwill be similar to what you see when ripping subtitles from DVDs. You can press Ctrl+Enter to fill in the Best Guess, then Enter to accept it, or press the Use button to do both in one step. You can press Ctrl+Left and Ctrl+Right to grow or shrink the text selection (the characters in the red selection rectangle) when you encounter disjoint characters - for example, when an 'O' is split into '(' and ')'. Also, just press Enter for white spots - background areas detected as subtitles such as the one in the red selection rectangle in the image above. This way, you are in fact telling SubRip to ignore similar looking white spots.
If at any time you see that the subtitles are no longer detected correctly, you may need to change the detection parameters. Press the Pause/Abort button in the main window, change them, then press the Continue button, just as when processing DVD subtitles. You may also press the Prev. button to go the first frame of the last subtitle in the video. This will erase the last subtitle from the text window, and re-run the detection with the new detection parameters.
Extract Subtitles From Dvd Ubuntu Media Player
If the same subtitle shows up more than once, you may continue to fill in the characters to train the OCR (exact duplicates will be detected and joined automatically), or you can press the Same As Last button to tell SubRip to go to the next subtitle. If a subtitle is repeated many times, you may need to modify the settings, either by increasing the Same sub tolerance value or by tweaking the Text, Outline and Fatten Tolerance values.
If the subtitles appear gradually, set the Skip first value to some number greater than 0 to skip that many frames before starting to accumulate frames. After Min. duration frames are accumulated, the next frames are just compared with the accumulated image. This speeds up the detection process. The Update every value tells SubRip to redo the accumulation process every that many frames. In accumulate mode, white pixels from different frames are ORed together (added), and in compare mode, white pixels from different frames are ANDed together (subtracted). Comparison is faster than accumulation, because no other processing is done besides thresholding color values, but may fail to detect when subtitles disappear if the background is entirely white. If this situation is encountered often in a video, just set the Update every value to 1+Min. duration to ensure that the compare mode is never used. This will slow down the recognition, so only use it if needed, otherwise leave the Update every value at 30 frames or so.
If you check the Save checkbox, a back and white bitmap (.pgm) file will be saved for each frame, containing only the characters that were recognized. The areas that were skipped (by pressing Enter in the New character(s) window for a NULL character) are not marked: notice that the white spots on the left side of the previous image are no longer present in the image below. The bitmaps, in combination with an index file, can be used later for subtitle removal.